The Ontario First Nations Technical Services Corporation (OFNTSC) is very pleased to announce that after three years in the making, the award-winning “First Nations Infrastructure Resilience Toolkit” (FN-IRT, or Toolkit) is completed and ready to use by First Nation communities. 
The FN-IRT, or Toolkit, allows First Nation communities to assess the vulnerability of their infrastructure, buildings, and facilities due to extreme weather. The Toolkit enables communities to forecast critical climate-related risks over the lifecycle of their assets, and provides guidance on how these risks can be integrated into long-term planning. The Toolkit also helps First Nations develop and implement sound asset management practices to forecast capital replacement and, operations and maintenance (O&M) investment needs, over the lifecycle of their assets. This allows First Nations to maximize the service life of their assets, while maintaining or improving levels of service.
The concept of the FN-IRT emerged from discussions between OFNTSC and Engineers Canada, regarding First Nations conducting their own climate vulnerability assessment using the recognized and widely used Public Infrastructure Engineering Vulnerability Committee (PIEVC) Protocol. The FN-IRT is now a recognized First Nation-specific assessment management tool and has been presented at the 2021 Triennial Conference of the Canadian, American and UK Societies of Civil Engineers.
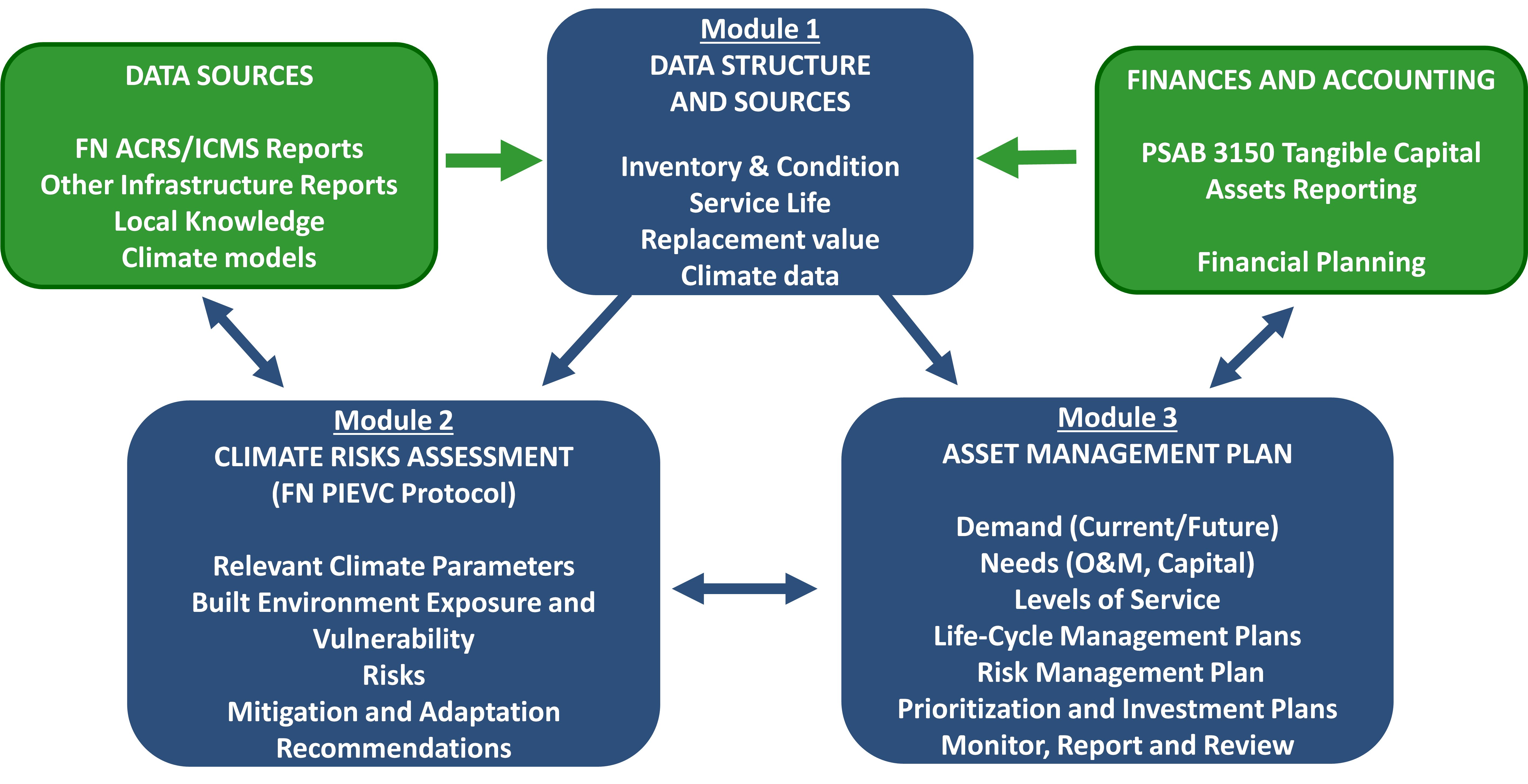
The Toolkit is comprised of three main modules and was developed based on current best practices and industry standards.
- Module 1 – Data Structure and Sources
- Module 2 – Climate Risk Assessment (CRA), also referred to as the First Nations Public Infrastructure Engineering Vulnerability Committee (FN-PIEVC)
- Module 3 – Asset Management Plan (AMP)
The Toolkit incorporates valuable asset information already available to First Nations in their infrastructure databases (ACRS, ICMS, PS 3150 TCA) and other relevant sources of information, such as housing reports and insurance statements. The Toolkit also allows for incorporating local and Traditional Knowledge to support changes to community levels of service, which may be required due to climate changes.
To enhance its credibility, the Toolkit aligns with industry best practices; in particular with the International Standards Organization (ISO) standard for risk management (ISO 31000:2018); CRAs (ISO 14091:2021) and asset management (IS0 5500x: 2014).
Module 1: Data Structure and Sources
Module 1 of the Toolkit focuses on completing a data register and processes to gather relevant information on the infrastructure for which the CRA will be performed, or an AMP can be prepared. This module serves as the foundation for Modules 2 and 3.
Module 2: Climate Risk Assessment
Module 2 of the Toolkit focuses on the process of completing a climate risk assessment and selecting the right assets and activities to be evaluated against climate impacts. Once these elements at risk have been identified, this module allows the review of past climate events that have caused disruptions, malfunctions, or failures to community infrastructure. This Module allows the user to establish risk profiles for the assets based on the current climate and future climate conditions.
The climate risk mitigation and adaptation measures identified can be integrated into Asset Management Plans.
Module 3: Asset Management Plan (AMP)
Module 3 of the Toolkit focuses on the process of completing an AMP using the information gathered in Modules 1 & 2. This module allows the user to identify asset lifecycle needs (e.g. O&M and rehabilitation requirements) and financial requirements to maintain and/or improve the service of an asset. In addition, this module allows the user to establish priorities, planning, monitoring, and reporting of all community infrastructure.


